Health
What are the different types of COVID-19 tests?
Laly Havern, PharmD, MS, BCACP, and Jen Matz, MPH Oct 21, 2025 • 6 min.
COVID-19 testing plays an important role in the ongoing effort to combat the virus. There are a number of COVID-19 tests on the market. Here you'll learn the basics on available COVID-19 tests, including when to be tested.
Types of COVID-19 tests
There are two types of COVID-19 tests:
- Diagnostic tests check for an active infection with COVID-19
- Antibody tests may be able to tell if you've had a past infection with COVID-19
Diagnostic tests
A diagnostic test will determine if you have an active COVID-19 infection. There are two classes of diagnostic tests:
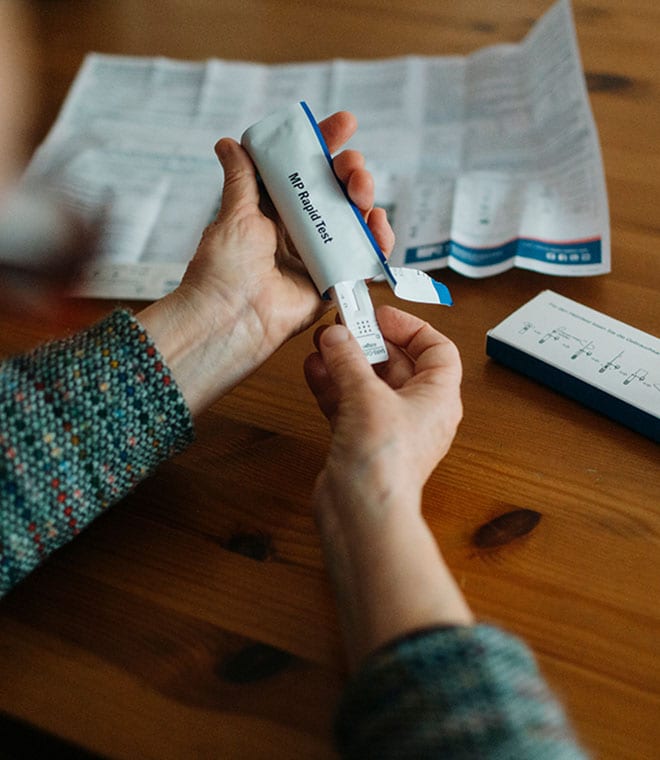
- Molecular tests (PCR, nucleic acid amplification tests, NAATs, and other molecular amplification tests) detect the genetic material of the virus. These tests are highly accurate and can detect COVID-19 even if you don’t have symptoms.
- Antigen tests (may also be called rapid COVID-19 tests or at-home COVID-19 tests) detect specific proteins on the surface of the virus. Antigen tests provide results more quickly than molecular tests, but they have a higher chance of false negatives (missing an active COVID-19 infection), especially when symptoms are not present. For most at-home COVID-19 tests, it's recommended to test again in 48 hours after a negative result—regardless of symptoms—to help reduce the chance of a false negative. If the result is still negative and you think you have COVID-19, you can test a third time after another 48 hours. Or you can get a molecular test or call your healthcare professional.
Some providers, offices and clinics can do antigen, molecular or combination testing for flu, COVID-19 and other select respiratory viruses at the same time using point-of-care tests. Other times, specimens need to be sent to a laboratory for testing.
For each test, you or your healthcare provider will use a special swab to collect samples from your nose or throat. You may even be asked to spit into a special tube. You may receive results the same day you were tested; however, most results take a few days to a week, depending on the type of test, lab and resources available.
Antibody tests
An antibody test is a blood test that checks for antibodies or immunoglobulins, which are proteins that are specific to each illness. Your body produces antibodies either in response to an infection or following vaccination.
If you receive a positive antibody test result, it could mean that you have antibodies from a past infection with COVID-19 or for being vaccinated against COVID-19. Antibody tests are not used to diagnose a current case of COVID-19.
If you receive a negative antibody test result, this may mean you never had COVID-19, or it may mean you had COVID-19 awhile ago, but the antibodies in your body decreased to undetectable levels.
|
Viral tests |
|
|
|
Molecular test |
Antigen test |
Antibody Test |
Also known as … |
Diagnostic test, nucleic acid amplification test, (NAAT), RT-PCR test, LAMP test |
Rapid diagnostic test, lateral flow test |
Serological or serology test |
What the test shows … |
Current COVID-19 infection |
Current COVID-19 infection |
May show previous infection or immunization against COVID-19 |
How the sample is taken … |
Nasal swab, throat swab or saliva (spit) |
Nasal swab, throat swab |
Fingerstick or blood draw |
Time to results … |
Same day to up to a week (depending on location) |
Same day, often in less than an hour (depending on location) |
Same day or up to 3 days (depending on location) |
Another test is … |
Not usually required |
Sometimes necessary if the results are negative. The provider may order a molecular test. |
Not usually required
|
The test does not … |
Show past infection |
Definitively rule out COVID-19 |
Diagnose COVID-19 |
Who should get tested for COVID-19?
According to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the following people should be tested for COVID-19:
- People with symptoms of COVID-19
- People who have been in close contact with someone with confirmed COVID-19
- People who are in certain high-risk settings, may need to test as part of a screening testing program.
You should also consider testing before coming into contact with someone who has a high risk for severe COVID-19, people who are older adults or immunocompromised, or have other medical conditions.
If you test positive for COVID-19, be sure to stay home, isolate from others, and seek follow-up care with your healthcare provider to determine what steps to take next.
Where can I get tested for COVID-19?
For additional information on COVID-19 testing at Walgreens, please visit https://www.walgreens.com/findcare/covid19/testing.
Clinically reviewed and updated by Amy Magil, October 2025.
Sources:
- https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/coronavirus-disease-2019-testing-basics
- https://www.cdc.gov/covid/testing/index.html
- https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/understanding-home-otc-covid-19-antigen-diagnostic-test-results
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronavirus/expert-answers/covid-antibody-tests/faq-20484429
- https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/antibody-serology-testing-covid-19-information-patients-and-consumers
- https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/home-covid-19-diagnostic-tests-frequently-asked-questions