Health
Staph infection: Causes, symptoms and treatment
By Dr. Anna H. Chacon, MD, Fellow of the American Academy of Dermatology Jun 17, 2025 • 8 min
Staph infection is the general term for an infection caused by Staphylococcus bacteria. These bacteria generally live on the skin and inside the nose of many people. However, if they enter the skin through a cut, scrape, wound or other skin injury, it can lead to an infection that can range from mild to severe. There are several types of staph infections. Each one has different causes, symptoms and treatments.
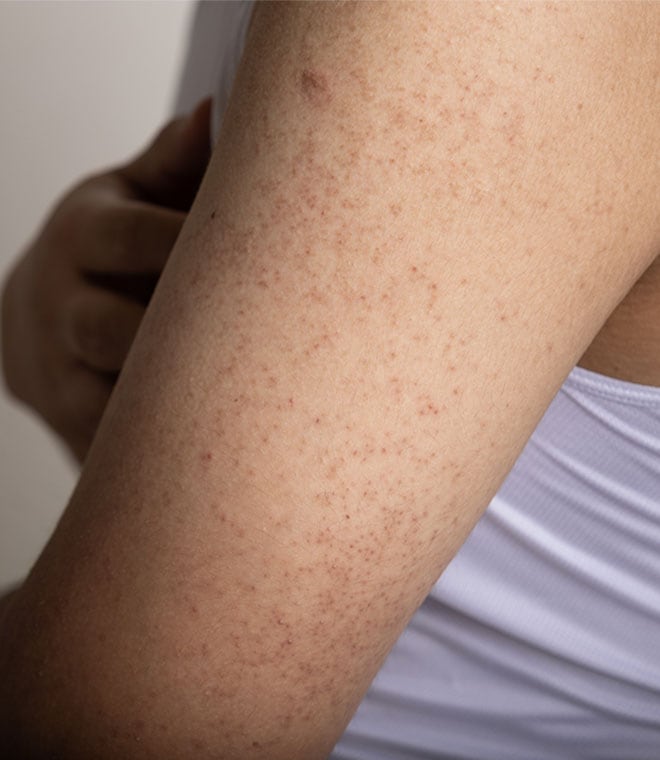
1. Boils: Although boils can be caused by many different factors, they’re most often the result of a staph infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus entering the skin. They are the most common type of staph infection. You’re most likely to develop boils on your face, neck, armpits, buttocks or thighs. However, they can develop anywhere. Boils caused by a staph infection can form clusters and spread to other areas of the body. They can also spread from person to person through close contact or from sharing different items like linens, clothes, athletic equipment, television controls and other personal items.
As a boil forms, skin becomes tender and sensitive, and you may experience itching. A fully formed boil appears as a red, painful, pus-filled bump with a yellow or white center. Boils often weep and crust over during the healing process. A fever and chills sometimes occur with the infection.
Treatment for boils depends on the severity. In most cases, boils will break open and heal on their own. However, your healthcare provider may make an incision to help a slow-healing, extremely painful or recurring boil drain and heal. Antibiotics may be prescribed in some cases.
2. Impetigo: Common in young children, impetigo is another skin infection typically caused by Staphylococcus aureus. It is contagious and can spread through close contact or from sharing personal items.
Symptoms of impetigo include:
- A blister filled with yellow or tan fluid that bursts easily
- Red skin surrounding the blisters
- Raw, shiny patches of skin that develop a yellowish-brown crust
- Swollen glands in areas near the rash
Healthcare providers typically prescribe topical or oral antibiotics to treat impetigo staph infections.
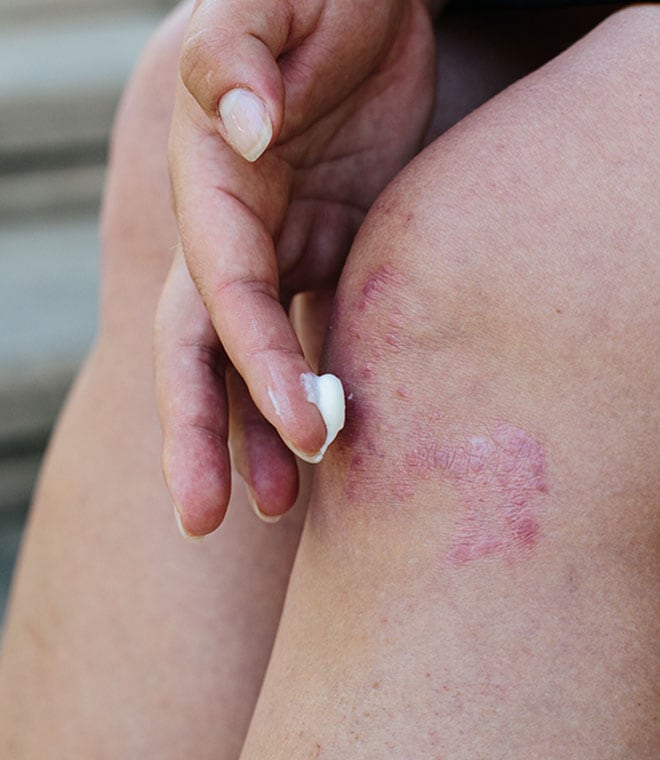
3. Cellulitis: An infection that occurs deep within the skin, cellulitis is frequently caused by Staphylococcus bacteria. However, it can also develop due to other forms of bacteria. It often occurs due to a wound, such as a surgical incision, cut, insect bite, animal bite, ulcer, tattoo or piercing.
Some common symptoms of cellulitis include:
- Red or dark discoloration of the skin
- Tenderness or pain
- Warm skin
- Inflammation of the skin
- Lumpy or pitted skin, similar in appearance to an orange peel
- Fluid-filled blisters
- Fever
- Chills
- Body aches
- Fatigue
Oral antibiotics are the most common treatment for cellulitis. Your healthcare provider may admit you to the hospital and prescribe intravenous (IV) antibiotics for a severe infection or if the infection doesn’t respond to oral medications.
4. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS): A serious skin infection, SSSS mostly affects infants and small children under 5. It develops when Staphylococcus aureus bacteria enter the skin and release toxins that injure the skin tissue.
SSSS usually begins with fluid-filled blisters that break open easily, leaving behind moist skin that feels tender and painful and resembles a burn. As the condition progresses, large areas of the top layer of skin begin to peel off. A fever often accompanies the skin rash.
In most cases, treatment for SSSS involves hospitalization. Healthcare providers typically prescribe IV antibiotics to treat the infection as well as IV fluids to prevent dehydration that may occur due to fluid loss from damaged skin.
5. Bacteremia: When staph bacteria enter the blood, they can cause a potentially serious infection called bacteremia. It most often occurs following a skin wound, or medical or dental procedure.
Early signs of bacteremia include fatigue and fever. If the infection goes untreated, additional symptoms may develop, including:
- Chills
- Diarrhea
- Low blood pressure
- Pain in the abdomen
- Rapid heart rate and breathing
- Vomiting and nausea
Antibiotics, usually taken orally, are the treatment for bacteremia. More serious infections may require hospitalization and IV antibiotics.
6. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS): A rare but serious infection, toxic shock syndrome, or TSS, happens when bacteria release toxins within the body. Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most common causes of TSS. However, not all TSS cases are staph infections.
TSS can occur due to wearing tampons for too long, so the infection is more common in women. However, TSS can also develop following surgery or an injury to the skin. Symptoms of TSS typically come on suddenly and may include:
- Body aches
- Chills
- High fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Rash that looks like a sunburn or appears as clusters of red dots
- Eye, mouth and throat redness
- Watery diarrhea
- Low blood pressure
- Peeling of skin on the palms and soles of the feet
Healthcare providers typically admit patients with TSS to the hospital to receive IV antibiotics. Additional treatments, such as medications to control blood pressure and surgical procedures to remove damaged tissue, may be necessary in some cases.
7. Food poisoning: A bacterial infection of the digestive system, food poisoning occurs when you eat food contaminated with bacteria. Many cases of food poisoning are due to staph bacteria.
Symptoms of food poisoning usually start within a few hours of eating contaminated food. They may include:
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Headache
- Stomach cramps
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting and nausea
- Weakness and fatigue
Food poisoning will often resolve on its own. Drinking plenty of fluids is important for preventing dehydration while you recover. In some cases, oral or IV antibiotics may be necessary to treat food poisoning from a staph infection.
8. Other types of staph infections: There are staph infections that can also impact other parts of the body, such as the heart valves (endocarditis), breast tissue (mastitis), bones (osteomyelitis) and lungs (bacterial pneumonia). Fever is a general symptom of staph infections, as is inflammation in or around the affected area. Antibiotics, administered orally or via IV, are usually the treatment for other types of staph infections. However, additional interventions may be necessary, depending on the location, symptoms and severity of the infection.
If you believe you have any type of staph infection, see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis and personalized treatment plan to prevent the infection from worsening.
Updated June 2025.
Sources:
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21165-staph-infection-staphylococcus-infection
- https://medlineplus.gov/staphylococcalinfections.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/staphylococcus-aureus/about/index.html
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/staph-infections/symptoms-causes/syc-20356221
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441868/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/boils-and-carbuncles-a-to-z
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/boils-and-carbuncles/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353776
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000860.htm
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15071-cellulitis
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000855.htm
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001352.htm
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/staphylococcal-scalded-skin-syndrome
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441979/
- https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/infections/bacteremia-sepsis-and-septic-shock/bacteremia
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000653.htm
- https://www.foodsafety.gov/food-poisoning
- https://www.cdc.gov/food-safety/signs-symptoms/index.html
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001652.htm